 English
EnglishThe role of nutrition in weight management for the elderly
Maintaining a healthy weight brings various health benefits, such as reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease, the risk of type 2 diabetes, and significantly improving bone and joint problems. Nutrition plays a key role, directly determining the weight and overall health of each person. For the elderly, nutrition becomes more important than ever, when the body begins to have changes in metabolism and absorption capacity. So, nutrition is able to help the elderly manage their weight effectively or not.
1. Overweight and obesity in the elderly and their health consequences
To assess whether weight is appropriate for height or not, we often use the body mass index (BMI). This index is calculated by taking the weight (in kilograms) divided by the square of the height (in meters). A high BMI is closely related to many serious health problems, including cardiovascular disease, overweight, diabetes, and vascular diseases, especially in the elderly. According to recommendations from the International Diabetes Federation & Western Pacific Region Organization (IDI & WPRO), older adults should maintain a BMI between 18.5 and 22.9 to ensure the best health.
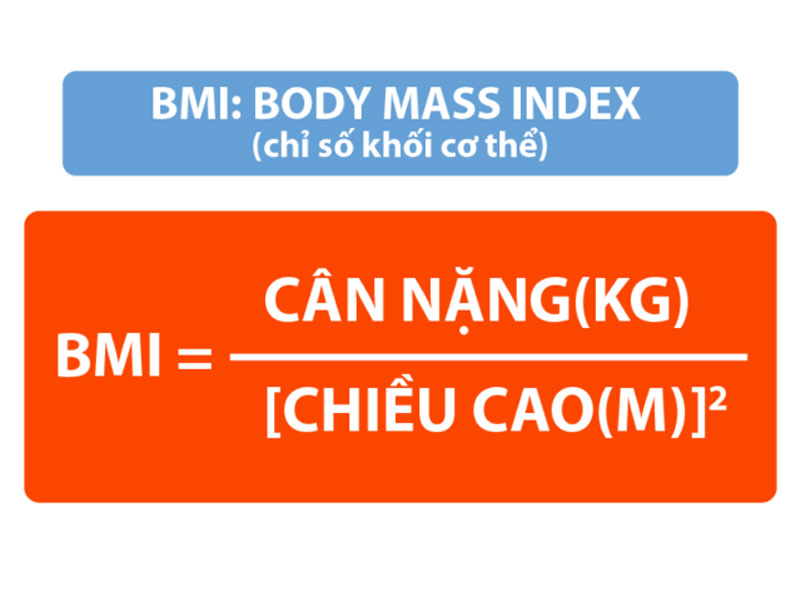
Body mass index (BMI) is closely linked to many serious health problems
Metabolism tends to slow down as people age. This means that older people burn fewer calories than when they were younger, even when they maintain the same level of activity. The main reason is a decrease in muscle mass, while the percentage of body fat increases, making the process of burning calories slower. In addition, hormonal changes also contribute to slowing metabolism. As a result, the elderly are more likely to accumulate excess fat and gain weight, even if their diet and physical activity levels do not change significantly.
Age also brings changes in mobility, causing older people to be less physically active. Bone and joint problems, decreased muscle strength, and chronic diseases can limit their mobility. As physical activity levels decrease, so do the body’s energy needs. However, if calorie intake remains the same or even increases, the excess energy will be stored as fat, leading to weight gain and obesity. This is a vicious cycle, as obesity is the cause of limited mobility, making the condition worse.

Older people are often less physically active
As we age, the energy needs decrease, by 20% for people aged 60 and 30% for people over 70 compared to 25 years old. However, the need for essential nutrients increases, especially protein (60-70 grams/day), B vitamins and calcium. This means that, instead of focusing on the quantity of food, older adults need to prioritize the nutritional quality of each meal.
Protein plays an important role in maintaining muscle mass, strengthening the immune system and supporting recovery from injury or surgery at all ages. However, many older adults do not consume enough protein, partly because they have difficulty chewing and swallowing protein-rich foods such as meat. Therefore, choosing foods that are rich in nutrients per calorie is extremely important. Prioritize foods rich in easily digestible protein and vegetables and fruits rich in vitamins. Minerals and rich sources of calcium to ensure comprehensive health for the elderly.
Being overweight or obese not only affects your appearance but also negatively impacts your mental and physical health. Overweight people often feel a lack of confidence, are afraid to communicate and limit their participation in social activities. According to statistics, obese people are 4 times more likely to have coronary artery disease, 6 times more likely to have a stroke, and 6 times more likely to have diabetes than people of normal weight. In addition, obesity also increases the risk of other diseases such as fatty blood, respiratory problems, hormonal disorders, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, gout, digestive disorders and memory loss.
2. The role of nutrition in weight management in the elderly
A scientific diet, ensuring enough energy, diversity, and balance of nutrients helps maintain life activities, supports the development and recovery of organs in the body, and limits the risk of non-communicable diseases at all ages, especially the elderly.
In the elderly, providing energy from food plays a key role in maintaining health and daily activities. Our bodies use energy from calories in food to perform basic functions such as breathing, blood circulation and movement. However, as we age, the metabolic rate often slows down, resulting in lower demand of calories for the body. Therefore, the elderly need to pay attention to maintaining a balance between calorie intake and calorie expenditure. Consuming excess calories more than needs can lead to weight gain and related health problems, while calorie deficiency can cause weakness and impaired body function.
Hormones such as insulin and leptin play an important role in regulating hunger and satiety in older adults. Insulin helps control blood sugar levels, while leptin signals the brain that the body has enough energy. Diet has a big impact on the activity of these hormones. For example, consuming too much sugar and refined starches can lead to insulin resistance, making it difficult to control weight and blood sugar. In contrast, a diet rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats may improve insulin sensitivity and increase feelings of fullness, thereby supporting effective weight management in older adults.
Choosing the right foods is important to boost metabolism and burn calories more efficiently in older adults. Spices such as ginger and turmeric also have metabolism-boosting effects. Beans, such as peas and lentils, are rich in fiber. In addition, whole grains also play an important role in supporting digestion and maintaining a reasonable weight. However, the elderly should also pay attention to choosing foods that are easy to digest and suitable for their health condition.

Ginger spice has the effect of stimulating metabolism
3. Common mistakes upon weight loss in the elderly
Weight loss in the elderly requires caution and scientific knowledge. Many elderly people make common mistakes such as fasting, using functional foods of unknown origin or applying an overly strict diet. These measures are not only ineffective but also have negative effects on overall health.
Fasting is not an effective and safe weight loss method for the elderly. As they age, the elderly body tends to lose muscle mass and bone density. Fasting can aggravate this condition, leading to weakness, a weakened immune system and an increased risk of osteoporosis. In addition, fasting can cause digestive problems, hypoglycemia and negatively affect mood. Instead of fasting, the elderly should focus on building a balanced, nutritious diet that meets the body’s needs to maintain health and control weight in a sustainable way.

Fasting is a common mistake in weight loss in the elderly
In addition, using functional foods of unknown origin is a serious mistake that the elderly should avoid. These products are often not tested for safety and effectiveness, may contain toxic ingredients or interact negatively with the medications they are taking. This is especially dangerous for the elderly, who often have many underlying medical conditions and are taking many different medications. Instead of taking risks with products of unknown origin, the elderly should consult a doctor or nutritionist for advice on safe and effective weight loss methods.
Extreme, strict diets often eliminate many important food groups, leading to nutritional deficiencies and negative effects on overall health. In addition, these diets are often difficult to maintain in the long term, leading to weight gain after stopping. The elderly should focus on a balanced, flexible diet that suits their personal preferences. It is important to make sustainable changes in lifestyle, including diet and physical activity, to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
4. How should the elderly eat?
For the elderly, eating is not only about meeting energy needs but also the key to protecting health and improving quality of life. Therefore, maintaining a healthy diet becomes extremely important. This article provides detailed instructions on how to establish a scientific diet suitable for the elderly.
The body’s energy needs decrease with age, but the need for essential nutrients increases. Therefore, the elderly need to choose foods that are rich in nutrients per calorie, ensuring adequate protein to maintain muscle mass, B vitamins to support nerve function, and calcium to protect bone and joint health. It is necessary to choose fresh, nutritious, and easy-to-digest foods to ensure comprehensive health.
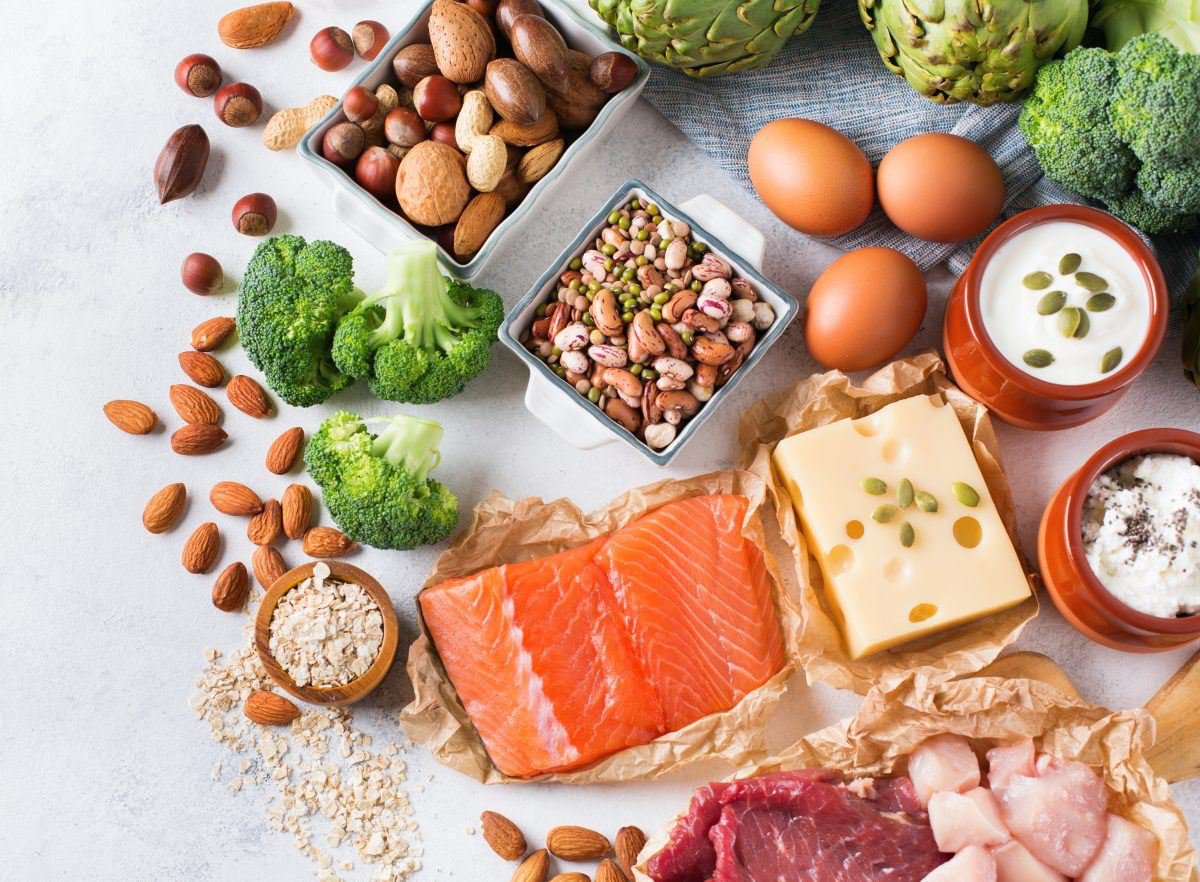

Foods rich in protein and calcium for the elderly
To create a healthy and suitable menu for the elderly, it is necessary to follow some basic principles.
First, diversify food by combining many types of food from different groups, ensuring adequate nutrition and balance.
Second, pay attention to the portion and frequency of meals as the secretion of gastric juice in the elderly’s body is often reduced, the process of digesting food is also longer.
Finally, create a comfortable and fun dining environment to increase appetite, promote digestion.
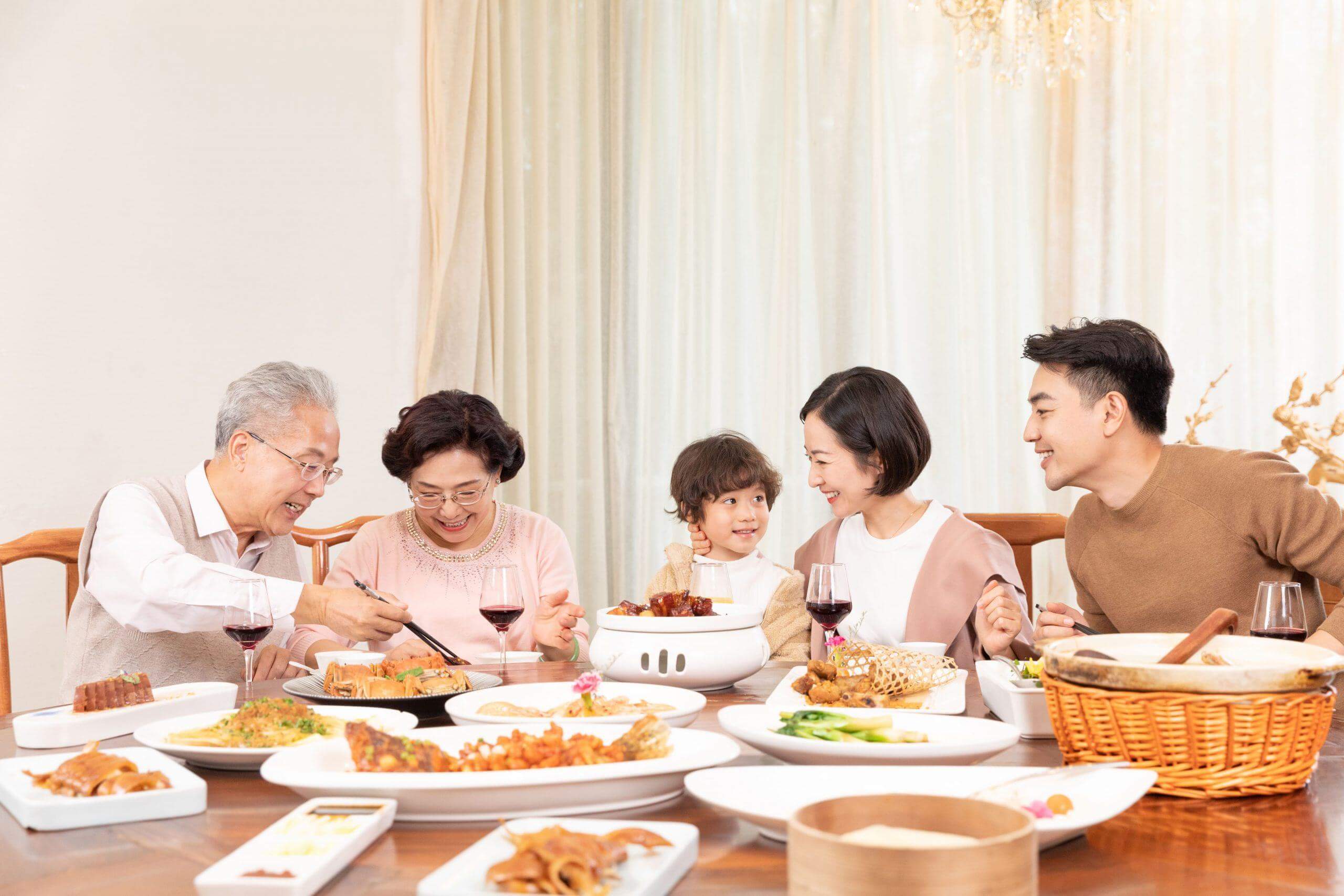

A happy family dining atmosphere makes meals more delicious
Sufficient water is an important factor that cannot be ignored in the elderly’s diet. Water accounts for more than ⅔ of the body, playing an essential role in maintaining basic body functions, including temperature regulation, nutrient transport, and calorie burning. As we age, the elderly’s sense of thirst may decrease, leading to the risk of dehydration. Therefore, it is necessary to actively drink water regularly, even when you do not feel thirsty. Keep a bottle of water next to you and take small sips throughout the day. In addition to filtered water, you can supplement water from fruits, vegetables, and soups.
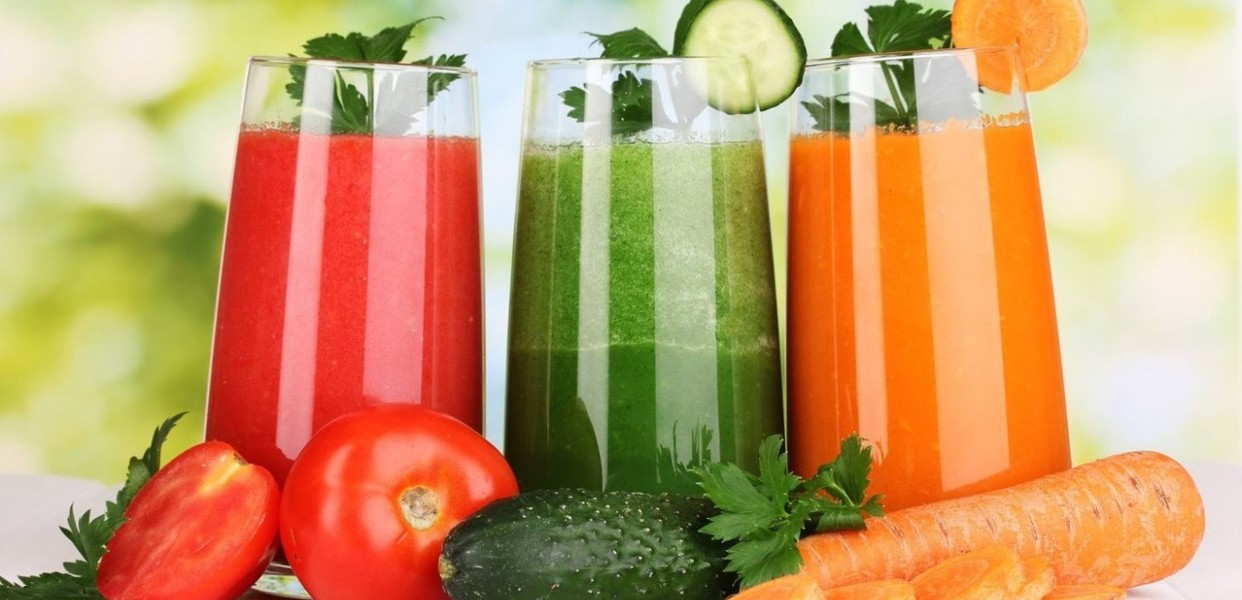

Hydrate the elderly through fruit and vegetable juice
For the most appropriate and safe diet, the elderly should consult a nutritionist. The expert will assess your health status, nutritional needs, and personal preferences to develop a scientific and effective eating plan. They also provide useful advice on food selection, food preparation, and weight management. Remember, each person has a different physical condition and nutritional needs, so expert advice is essential.
Conclusion: The key role of nutrition in controlling the weight of the elderly is undeniable. Weight management through nutrition is not a short-term journey but requires perseverance and persistence over time. However, these efforts worth it with great health benefits, bringing the elderly a happy and healthy life, allowing them to enjoy their old age years to the fullest. Remember, every small change in diet contributes to making a big difference to overall health.
